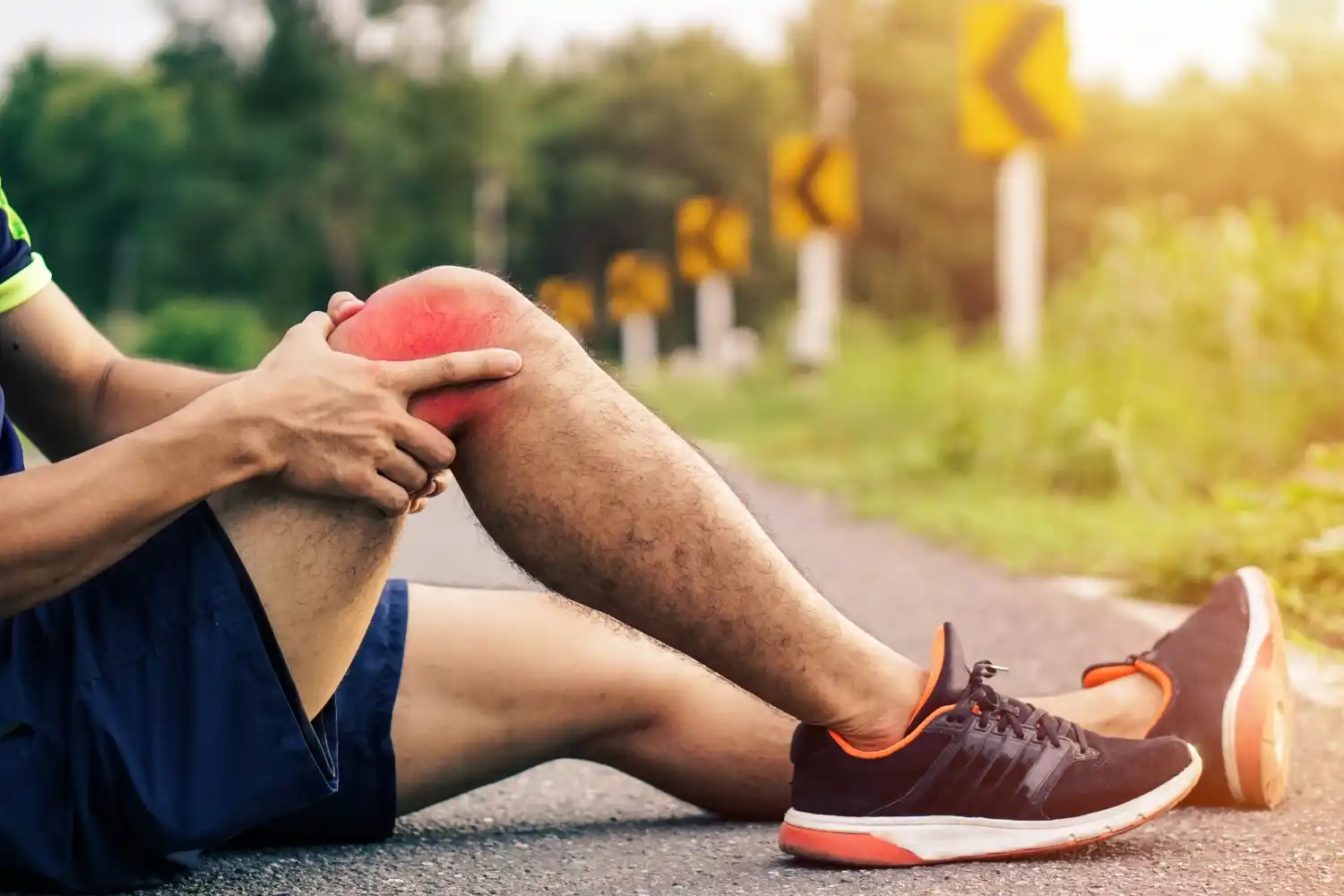
Sports and physical activities are excellent for maintaining health, fitness, and mental well-being. However, they also come with the risk of injuries. Prevention of sports injuries in chennai is crucial to ensure athletes and fitness enthusiasts can continue enjoying their activities without setbacks. By understanding the risks and adopting preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their chances of getting injured.
Sports injuries happen during physical activities, whether you’re a professional athlete or just exercising for fun. These injuries can range from minor sprains to serious fractures, and they can significantly impact your ability to stay active. Understanding how to manage these injuries helps in avoiding long-term damage and getting back to your favorite activities sooner.
Sports injuries occur when excessive force or stress is placed on muscles, bones, ligaments, or tendons during physical activities. They can result from accidents, improper training techniques, lack of warm-up or stretching, or using the wrong equipment. Overuse injuries, like tendonitis, also happen when the same movements are repeated too often.
What Are Sports Injuries?
Sports injuries refer to physical damage that occurs during sports or exercise. They can range from minor bruises to severe ligament tears or fractures. Prevention of sports injuries involves taking proactive steps such as proper warm-ups, wearing protective gear, and following correct techniques. These injuries can happen due to external impact, overuse, or improper body movements, making awareness and preparation key elements in reducing risks.
Types of Sports Injuries
- Chronic Injuries: These develop over time due to repetitive stress on a specific body part. Conditions like tendonitis or stress fractures start with mild pain that gradually worsens.
- Acute Injuries: Sudden injuries that happen during an activity, like a sprained ankle or a broken bone. These injuries usually cause immediate pain, swelling, and bruising.
First Aid for Sports Injuries
- Immediate first aid is crucial: for the prevention of sports injuries in Chennai, especially to minimize damage and begin early recovery.
- RICE method: (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) is widely recommended as an effective first step after a sports injury.
- Rest: helps protect the injured area and avoid further strain or worsening of the condition.
- Ice application: reduces swelling and numbs pain when applied within the first 24-48 hours post-injury.
- Compression: using elastic bandages helps control swelling and offers light support to the injured part.
- Elevation: above heart level decreases fluid accumulation and promotes faster healing.
Knowing and applying these steps promptly is key to effective first response and long-term prevention of sports injuries in Chennai.
Common Sports Injuries
Understanding the specific types of sports injuries helps in better prevention and management. Here are some of the most common injuries:
- Sprains and Strains: Sprains involve overstretching or tearing ligaments, often in the wrists, ankles, or knees. Strains affect muscles or tendons, usually from overstretching or overexertion.
- Fractures: Breaks in the bone that can range from tiny stress fractures to complete breaks. High-impact sports like football or basketball often result in fractures.
- Dislocations: Occur when bones are forced out of their normal positions, common in contact sports like football. This injury causes significant pain and swelling and needs immediate medical attention.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation or irritation of a tendon due to repetitive motions, often affecting the shoulders, elbows, or knees.
- Concussions: Traumatic brain injuries from a blow to the head, common in contact sports like football or boxing. Proper management is crucial to prevent long-term effects.
Causes of Sports Injuries
The causes of sports injuries vary based on the sport, the individual, and external conditions. Common causes include:
- Poor Training Techniques – Incorrect posture, body mechanics, or form can put unnecessary stress on muscles and joints.
- Lack of Warm-up and Stretching – Cold muscles are less flexible and more prone to strains, making proper warm-ups essential before intense physical activity.
- Overuse and Repetitive Motion – Continuous stress on joints and muscles can lead to chronic injuries such as stress fractures and tendonitis.
- Improper Equipment or Gear – Using the wrong shoes, worn-out gear, or inadequate protective equipment increases injury risks.
- Fatigue and Overexertion – Pushing beyond physical limits without proper rest can lead to muscle breakdown, stress fractures, and exhaustion.
- Environmental Factors – Playing on uneven surfaces, in extreme weather conditions, or on slippery grounds can lead to falls and other injuries.
By addressing these causes of sports injuries, individuals can significantly reduce their risk and improve their athletic performance.
Sports Injury Prevention Tips
The prevention of sports injuries involves following best practices to keep the body safe during exercise. Here are some essential tips:
1. Warm-Up and Cool Down Properly
- Perform dynamic stretching before sports to prepare muscles and joints.
- Engage in light jogging or mobility exercises to increase circulation.
- Cool down with static stretching to prevent stiffness and soreness post-activity.
2. Use Proper Techniques
- Learn the correct form and posture for each sport to minimize unnecessary stress on the body.
- Seek guidance from professional coaches or trainers to develop efficient movement patterns.
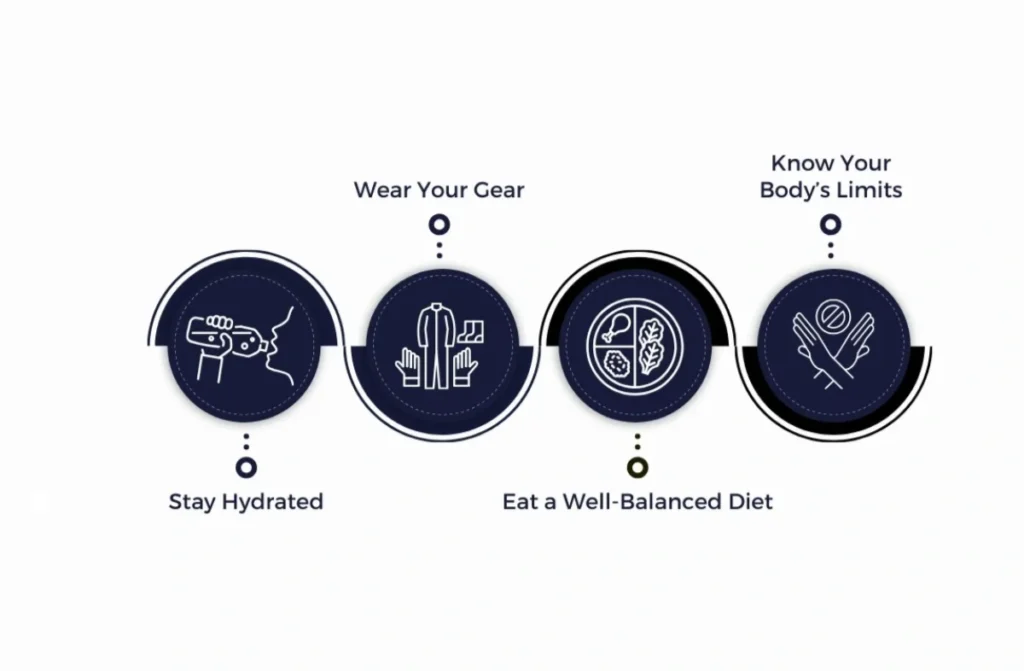
3. Wear Protective Gear
- Helmets, knee pads, wrist guards, and mouthguards significantly reduce impact-related injuries.
- Choose sport-specific footwear with adequate arch and ankle support for stability.
4. Stay Hydrated and Maintain Nutrition
- Drink sufficient water before, during, and after exercise to prevent dehydration and muscle cramps.
- Consume a balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals to support muscle repair and energy levels.
5. Strength and Conditioning Training
- Strengthening muscles helps stabilize joints and prevent excessive strain.
- Regular flexibility exercises improve range of motion and reduce stiffness, lowering the risk of injuries.
6. Avoid Overtraining
- Listen to your body and rest when necessary to avoid burnout.
- Gradually increase intensity instead of making sudden, drastic changes to prevent stress injuries.
7. Follow a Recovery Plan
- Take scheduled breaks between intense workouts to allow muscle healing.
- Apply ice or heat therapy to soothe sore muscles and reduce inflammation after strenuous activity.
Following these sports injuries treatment in kolathur and prevention strategies ensures a safer and more enjoyable sports experience while minimizing downtime due to injuries.
Sports Injury Treatment
Prevention of sports injuries in Chennai starts with timely intervention and expert care. For any significant or persistent sports injury, consulting a qualified medical professional is essential. Early diagnosis, tailored treatment plans, and proper rehabilitation not only speed up recovery but also help avoid complications that could lead to surgery. Staying proactive with injury management ensures long-term performance, minimizes downtime, and protects your overall health and mobility.
Treatment Options: Surgical and Non-Surgical
Sports injury treatment depends on the type and severity of the injury. Here’s an overview of the options:
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and techniques to restore function, improve mobility, and strengthen the injured area.
- Medications: Pain relievers like ibuprofen to manage pain and inflammation.
- Rest and Immobilization: Using braces, splints, or casts to keep the injured area stable while it heals.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation in cases like tendonitis.
Surgical Treatments
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure to diagnose and treat joint problems.
- Ligament Reconstruction: Surgery to repair severe ligament injuries like ACL tears.
- Fracture Fixation: Surgery to realign and stabilize broken bones using plates, screws, or rods.
- Tendon Repair: Surgery to reattach a ruptured tendon, like the Achilles tendon, to the bone.
Precautions
Preventing sports injuries is just as important as treating them. Here are some tips to stay safe:
- Proper Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Dynamic stretching before and static stretching after exercise help prevent injuries.
- Use of Proper Equipment: Wear the right footwear and protective gear for your sport.
- Awareness and Education: Understand the risks of your sport and learn how to minimize them with proper techniques.
Conclusion
The prevention of sports injuries in chennai is essential for athletes of all levels. By understanding the causes of sports injuries, recognizing the types of sports injuries, and following preventive measures, individuals can stay active and injury-free. Whether engaging in professional sports or recreational activities, prioritizing safety, proper training, and recovery will lead to better performance and long-term health. Consistency in adopting these preventive measures will help athletes continue enjoying their sport while reducing injury risks significantly.
Read also: Soft Tissue Injuries


