Pelvic & Acetabular fracture fixation in chennnai is a specialized surgical procedure designed to stabilize and repair fractures in the pelvic and hip regions. These injuries, often caused by high-impact trauma, require prompt and precise treatment to restore function, reduce pain, and prevent long-term complications. Patients looking for pelvic & Acetabular fracture fixation in Chennai can benefit from timely diagnosis and advanced orthopedic care.
Understanding Pelvic and Acetabular Fracture Fixation
Pelvic and acetabular fractures are severe injuries that typically result from high-impact trauma, such as car accidents or significant falls. The pelvis and acetabulum (the socket of the hip joint) are critical structures that support the body’s weight and enable movement. Fractures in these areas require prompt and specialized treatment to restore function and prevent long-term complications. Pelvic & acetabular fracture fixation in Chennai offers specialized care to facilitate proper healing and recovery.
Why Early Intervention is Crucial
Due to the complexity and importance of the pelvic and acetabular regions, immediate medical intervention is essential. Without proper treatment, these fractures can lead to complications such as chronic pain, deformity, and impaired mobility. Surgical fixation ensures that the bones heal correctly, allowing patients to regain their normal activities. Early access to advanced pelvic & acetabular fracture fixation in Chennai can improve long-term results and reduce the chances of complications.
Types of Pelvic and Acetabular Fractures
Identifying Different Types of Fractures
Pelvic and acetabular fractures can vary in severity and type, each requiring a different approach to treatment. Common types include:
- Stable pelvic fractures: Involve a single break in the pelvic ring, where the bones remain aligned.
- Unstable pelvic fractures: Multiple breaks or a break that displaces the pelvic bones, often requiring surgical intervention.
- Acetabular fractures: These fractures involve the socket of the hip joint, which can significantly impact the stability and function of the hip.
For those needing pelvic & acetabular fracture treatment in Chennai, proper identification of fracture type is essential to guide care.
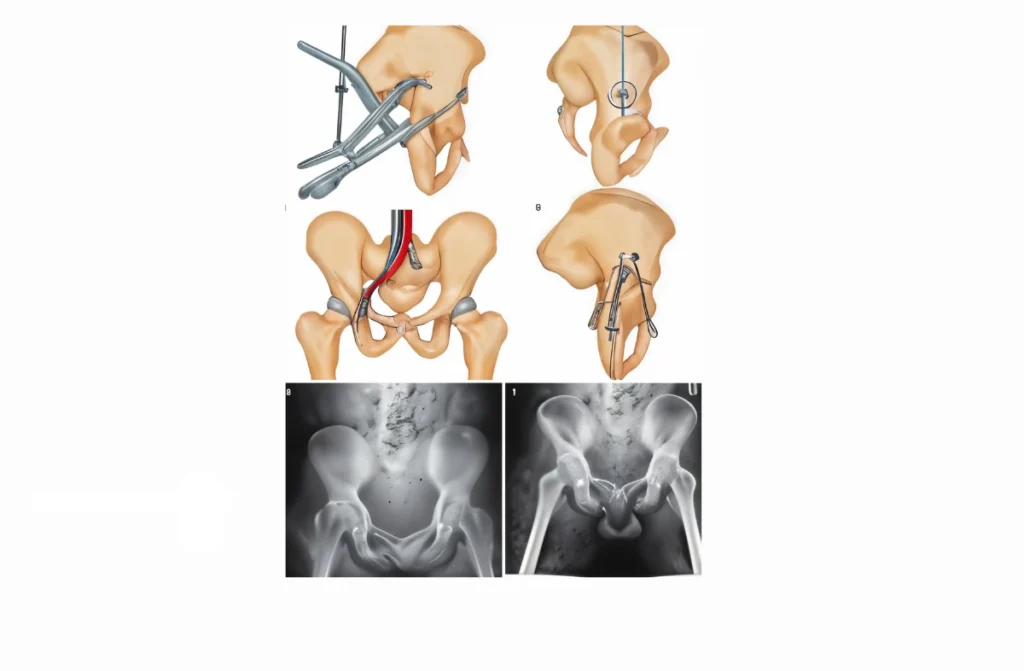
Diagnosis and Assessment
Accurate diagnosis through imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs is essential for determining the type and extent of the fracture. This allows the orthopedic surgeon to plan the most appropriate treatment strategy for pelvic & acetabular fracture fixation in Chennai.
Factors Affecting Treatment Choic
- Location of the fracture: The specific area of the pelvis or acetabulum that is fractured will guide the surgical approach.
- Severity of the injury: More severe fractures may require extensive surgical fixation and a longer recovery period.
- Patient’s overall health: Consideration of the patient’s age, bone density, and overall health is important in planning the surgery.
Surgical Fixation Techniques
Approaches to Pelvic and Acetabular Fracture Fixation
Surgical fixation of pelvic and acetabular fractures involves various techniques depending on the nature and severity of the fracture. The main goal is to restore the normal anatomy of the pelvis and acetabulum and to stabilize the bones to promote healing.
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): A common procedure where the fractured bones are realigned and fixed in place with screws, plates, or rods.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: In some cases, less invasive techniques may be used, involving smaller incisions and specialized instruments to reduce recovery time.
- Bone Grafting: Used in cases where bone loss has occurred, bone grafts may be required to support the structure and promote healing.
Pelvic & acetabular fracture surgery in Chennai offers advanced options tailored to the patient’s needs.
Advantages of Surgical Fixation
- Stabilization of fractures: Prevents movement of the bones, allowing them to heal in the correct position.
- Pain relief: By stabilizing the fracture, surgery often provides significant pain relief.
- Restoration of function: Surgical fixation aims to restore the normal function of the hip and pelvic region, enabling patients to resume their daily activities.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
Postoperative Care Following Pelvic and Acetabular Fracture Fixation
After surgery, proper postoperative care is crucial for a successful recovery. This includes:
- Pain management: Medications are prescribed to manage pain and ensure patient comfort during the initial recovery period.
- Wound care: Keeping the surgical site clean and dry is essential to prevent infection.
- Physical therapy: Early mobilization through guided physical therapy helps in regaining strength and flexibility.
Rehabilitation Process
The rehabilitation process is tailored to the individual, focusing on gradually restoring mobility and strength. It typically involves:
- Weight-bearing restrictions: Depending on the severity of the fracture, weight-bearing may be restricted for several weeks to allow proper healing.
- Strengthening exercises: Specific exercises are introduced to strengthen the muscles around the hip and pelvis.
- Mobility aids: The use of crutches or walkers may be necessary initially, with a gradual transition to independent movement.
Regular follow-up is a key part of pelvic & acetabular fracture treatment in Chennai, ensuring proper healing and progress.
Monitoring Recovery Progres
Regular follow-up appointments with the orthopedic surgeon are important to monitor the healing process, adjust the rehabilitation plan as needed, and address any complications that may arise.
Benefits and Risks
Benefits of Pelvic and Acetabular Fracture Fixation
Surgical fixation of pelvic and acetabular fixation in kolathur offers several significant benefits:
- Improved stability: The procedure stabilizes the fracture, reducing the risk of further injury and complications.
- Enhanced mobility: Proper fixation allows patients to regain full or near-full mobility, improving their quality of life.
- Reduction in chronic pain: By addressing the fracture correctly, many patients experience a significant reduction in long-term pain.
Balancing Benefits Against Risks
When considering pelvic & acetabular fracture fixation in Chennai, it is important to weigh the significant benefits of improved stability, mobility, and pain relief against the potential risks. With proper care and a comprehensive rehabilitation plan, many patients achieve successful outcomes.
Conclusion
Pelvic and acetabular fracture fixationin kolathur is a critical procedure for restoring stability, function, and mobility in patients who have suffered severe fractures in these complex regions. By addressing the fractures through specialized surgical techniques, patients can significantly reduce the risk of long-term complications such as chronic pain, deformity, and impaired mobility.
With a comprehensive rehabilitation plan and adherence to medical advice, most patients can expect to regain their independence and return to daily activities with minimal discomfort. Pelvic & acetabular fracture fixation in Chennai offers a path to recovery that can lead to a better, more active life.
Read also: Arthroscopic Hip Reconstruction Surgery