Arthroscopic Ankle Reconstruction Surgery in Chennai is a minimally invasive procedure designed to restore ankle stability, reduce pain, and improve overall function. For individuals dealing with chronic ankle instability, repeated sprains, or post-injury complications, this modern surgical option offers lasting relief and a faster return to normal activity. Patients in and around Kolathur can now benefit from this advanced treatment under the expert care of Dr. Omer Sheriff.
What is Arthroscopic Ankle Reconstruction?
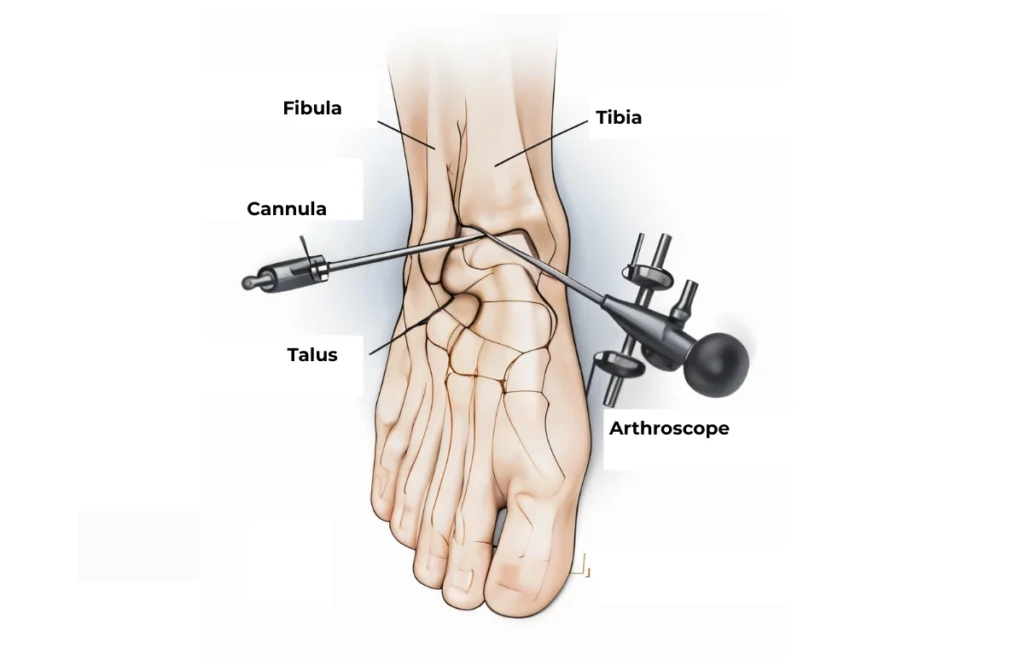
Arthroscopic ankle reconstruction is a surgical technique that uses a small camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments inserted through tiny incisions around the ankle. This method allows surgeons to view and repair damaged ligaments, remove debris, and restore joint function without the need for large open incisions. Compared to traditional surgery, this approach leads to less pain, minimal scarring, and quicker recovery—making it ideal for both athletes and everyday individuals with ankle injuries.
Who Needs This Surgery?
This procedure is typically recommended for patients who experience:
- Chronic ankle instability
- Frequent or recurring ankle sprains
- Torn or stretched ligaments
- Pain during walking, running, or sports
- Stiffness or persistent ankle swelling
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, especially after conservative treatments have failed, arthroscopic ankle replacement surgery in Kolathur may be the right next step toward long-term relief and stability.
Why Early Treatment Matters
Delaying treatment for ankle instability or ligament injuries can lead to progressive joint damage, arthritis, or permanent loss of mobility. Early intervention with Arthroscopic Ankle Reconstruction Surgery in Chennai helps preserve joint function, prevents further deterioration, and allows for a smoother recovery. Addressing the issue early on also improves surgical outcomes and reduces the risk of needing more invasive procedures in the future.
Conditions Treated with Arthroscopic Surgery
This minimally invasive technique is highly effective for treating a variety of ankle conditions, including:
- Torn or stretched ankle ligaments
- Osteochondral lesions (cartilage and bone damage inside the joint)
- Loose bone or cartilage fragments causing joint locking
- Post-injury pain or chronic inflammation
If you are considering Arthroscopic ankle Reconstruction treatment in Chennai or exploring advanced options like Arthroscopic Ankle Reconstruction Surgery in Chennai, this approach offers proven outcomes with minimal downtime.
How the Procedure Works
During the surgery, the orthopedic surgeon makes 2–3 small incisions near the ankle. An arthroscope is inserted to view the joint in real-time on a monitor. Using precise instruments, the surgeon repairs or reconstructs damaged ligaments, removes loose fragments, and smooths cartilage if necessary. The procedure typically lasts 60 to 90 minutes and is often performed as a day-care surgery, allowing most patients to return home the same day.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Following Arthroscopic Ankle Reconstruction Surgery in Chennai, a structured rehabilitation plan is crucial for full recovery. Here’s what to expect:
- Initial rest and immobilization: A brace or cast is used to support healing.
- Physical therapy: Gradual exercises begin to restore flexibility and build strength.
- Return to activity: Most patients resume walking in a few weeks and return to full sports in a few months, depending on healing and physical therapy progress.
For some patients, ankle joint arthroscopic surgery in Kolathur may also be an alternative or complementary option, especially if multiple ankle issues are present.
Benefits of Arthroscopic Ankle Reconstruction
Choosing arthroscopic reconstruction over traditional open surgery offers several patient-friendly advantages:
- Minimal scarring due to smaller incisions
- Reduced risk of infection and complications
- Faster return to work, sports, or daily activities
- Long-term ankle stability and improved range of motion
- Lower chance of future sprains or joint damage
With Arthroscopic Ankle Reconstruction Surgery in Chennai, patients can expect a safe, effective, and recovery-focused solution to chronic ankle conditions.
Why Choose Dr. Omer Sheriff in Kolathur
Dr. Omer Sheriff is a trusted orthopedic specialist known for his precision in arthroscopic and sports injury surgeries. Patients from Kolathur and across Chennai choose him for his personalized care, advanced techniques, and deep commitment to patient recovery. Whether you’re seeking Arthroscopic ankle replacement surgery in Kolathur or ankle joint arthroscopic surgery in Kolathur, Dr. Omer’s expertise ensures a tailored and effective treatment plan that supports your long-term joint health.
Conclusion
If ankle instability or chronic pain is limiting your daily life, don’t wait. Arthroscopic Ankle Reconstruction Surgery in Chennai offers a minimally invasive, high-success solution to restore movement, comfort, and confidence. With expert guidance from Dr. Omer Sheriff and modern surgical care available locally in Kolathur, you can take the first step toward pain-free mobility and long-term ankle health. Schedule your consultation today to begin your recovery journey.


